Recent Advances And Novel Strategies in Liposome Formations for Drug And Nutraceutical Delivery
Lisha Zhao
Postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Chemical Engineering, McMaster University
Keywords: Liposome, Encapsulation, Drug delivery, Novel strategy
Recently, the development of novel encapsulation systems to deliver drugs and nutraceuticals for enhanced stability and bioavailability has drawn growing attention [1]. Liposome is one of promising encapsulation systems to deliver a number of drugs, bioactives and nutraceuticals. Liposomes are versatile colloidal nanovesicles composed of one (or more) bilayer of phospholipids surrounding an aqueous core. Hydrophobic, hydrophilic and/or amphiphilic compounds can be encapsulated into liposomes for various applications. Due to the similarity to natural cell membranes, liposomes show great biocompatibility and biodegradability for delivery purposes. Liposomes have played significant roles in diagnosis and treatment of a variety of diseases as one of most powerful delivery systems, and quire recently, have also drawn increasing attention in nutraceutical, food and cosmetic industry [2-3].
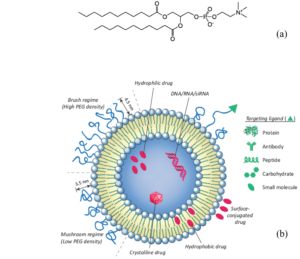
Figure 1: Chemical structure of phospholipids (a) and conformation structure and design of liposomes for drug delivery applications (b) [4].
Encapsulation of drugs or bioactives into liposomes can bring about following advantages: (1) protecting the encapsulated agents against unfavorable external conditions, such as light, heat, specific enzymatic degradation; (2) reducing the potential side effects and targets delivery to specific organs (2) improving the cellular uptake for enhanced efficacy and bioavailability; (3) controlling the release and modulated circulation of drugs and bioactives by the regulation of particle properties. At present, tradition lab-scale preparation methods to produce liposomes include thin film hydration, ethanol injection, reverse phase evaporation and detergent depletion methods. Since the traditional methods usually result in low reproducibility and heterogeneity in particle size distribution, several innovative preparations such as dual asymmetric centrifugation, cross-flow filtration detergent depletion, microfluidic hydrodynamic focusing and supercritical fluid preparation have been developed to overcome the drawbacks in traditional preparation and gained considerable success [5].
Although with a number of merits, liposomes still have a few challenges in their formulations. The low encapsulation efficiency for hydrophilic compounds, instability of phospholipid membrane and drug leakage as well as hydrolysis of ester bonds during long term storage still need to be resolved by using novel strategies. Active or remote loading using adjusted pH or ionic gradients have been developed to significantly increase the encapsulation efficiency and even retention rate to achieve enhanced efficacy of hydrophilic drugs. Incorporation of cholesterol or phytosterols into the bilayers works to modulate the membrane permeability and reduce the leakage of encapsulated agents. The application of synthetic phospholipids with functional groups or polymer combinations facilitates the stimuli-responsive properties in vesicles [6] and allows modulation of release properties. In addition, addition of synthetic inorganic or polymer nanoparticles to stabilize liposomes has emerged as a promising strategy to create hybrid vesicular systems [7]. With increasing innovative strategies, liposomes show great premise in biomedical and nutraceutical applications and have a bright future with many novel possibilities as a powerful delivery system.
References
- Nair, H.B., Sung, B., Yadav, V.R., Kannappan, R., Chaturvedi, M.M. and Aggarwal, B.B.. Delivery of antiinflammatory nutraceuticals by nanoparticles for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Biochemical pharmacology 2010, 80(12):1833-1843.
- Shade C.W. Liposomes as Advanced Delivery Systems for Nutraceuticals. Integrative Medicine: A Clinician’s Journal 2016, 15(1):33-36.
- Bozzuto, G., Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2015, 10:975-999.
- Çağdaş, M., Sezer, A.D. and Bucak, S. Liposomes as potential drug carrier systems for drug delivery. In Application of nanotechnology in drug delivery, Sezer, A.D., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2014.
- Zhao, L. and Temelli, F. Preparation of liposomes using a modified supercritical process via depressurization of liquid phase. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids 2015, 100:110-120.
- Xing, H., Hwang, K. and Lu, Y. Recent developments of liposomes as nanocarriers for theranostic applications. Theranostics 2016, 6(9):1336-1352.
- Yang, C. and Fu, Z.X. Liposomal delivery and polyethylene glycol‑liposomal oxaliplatin for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Biomedical reports 2014, 2(3):335-339.
Post Reviews:
No reviews yet...









